I am going to go see Hamilton this weekend, and I have been invited to share my impressions of the award-winning musical on a local NPR-affiliate the week following. I will be teaching the American Revolution next semester, and as some of my posts over the past several months make clear, I have been thinking about the stories we should tell quite a bit.
I have also been thinking a lot about the American constitutional system that emerged from that Revolution, what the Founders intended, and what they might think about our current mess. I have never thought much of “Framer’s Intent” as a style of constitutional argument that carries much weight, but still, we are historians, and comparisons for us come easily.
We have a president elected by a minority of the voters whose administration shows levels of mendacity, greed, and spite that stand in stark contrast to that of his predecessor. The president’s supporters work to restrict the right to vote of poor people and peoples of color out of fear that these constituencies will vote against him. Some of his sycophants, led by the besotted Jerry Falwell, Jr., have suggested that the president unconstitutionally extend his term. Indeed, the Democratic Speaker of the House Nancy Pelosi expressed her belief that the President will not voluntarily leave office if he loses the election. Meanwhile, the Attorney-General of the United States and the Secretary of the Treasury defy subpoenas from the House of Representatives, that chamber of the legislature that most directly represents the American people.

THE REVOLUTIONARY GENERATION believed that republican forms of government were inherently fragile because they relied upon the wisdom and the civic-mindedness of “the people.” The revolutionary generation, as historians like Bernard Bailyn, H. Trevor Colbourn, and Gordon Wood showed long ago, had no reason to expect that a republic could last forever and, indeed, all the examples they could point to had descended into tyranny and corruption. Perhaps our time is running out, I sometimes think. Perhaps we have had a good run that now is ending. I legitimately worry that the American constitutional system will not survive my children’s generation in any meaningful or recognizable form. The system is broken, as so many politicians have pointed out. It is broken because cynical, cowardly, and corrupt Republicans, aided by timorous Democrats, smashed it to pieces.
The Revolutionary generation believed that the purpose of government was to secure the Commonwealth, the good of the whole. In order to pursue the good of the whole, citizens must exercise and practice virtue. A virtuous citizen, in the parlance of the time, was one who could set aside his or her narrow self-interest and willingly make sacrifices for the good of the whole. Corruption, in this sense, was the exact opposite of virtue. In order to practice virtue, citizens required independence. They could not be subject to the will of another. That is part of the reason why women (subject to the authority of their fathers and husbands), tenants (subject to their landlord’s authority) and wage-earners (subject to their employers) could not vote in elections. In addition to independence, citizens had to remain active. They had to practice citizenship. They had to inform themselves, remain vigilant, because liberty was a fragile thing. A supine and ill-informed citizenry made fit-tools for tyrants.
While agreeing broadly that these concepts were important, the revolutionary generation could disagree intensely over what these terms meant. But few questioned the importance of these values. Commonwealth, Virtue, Independence, and Citizenship: by these standards we are not doing very well.
The Trump Administration has revealed itself as a smash-and-grab operation operated by liars and grifters. The Republican Party has become a haven for hacks and fools, an unholy alliance of the super-rich and the ill-informed. The President who proudly proclaimed his love for the “poorly-educated” on the campaign trail treats government as little more than an opportunity to generate wealth for his family and bile against those he views as enemies. He lies ferociously. He casts his legitimate critics as “enemies of the people.” He calls names. He vilifies. For him there is no common good. He is incurious and unlettered, a brute and a tyrant. He knows nothing of the Revolution or the Constitution.
Of course, there are Republicans who believe that we are part of something larger than a political party. There are patriotic Republicans who disagree intensely with Trump’s policies and behavior. But none of the Republicans holding office have had the courage to oppose him in any meaningful manner. Instead, they furrow their brows, hold their noses, and dive headfirst into the cesspool, the smell of the crap no longer bothering them once they are in.

Tens of millions of people continue to support the President, seemingly unaware of his administration’s utter contempt for the Constitution. Some of them embrace the President’s politics of spite. They find room under his big, hateful tent to express their own fears, and a racism nourished by the fevered rants of the megalomaniac who stumbled into the White House. Perhaps his fervent supporters know so little about the Constitution, and their civic illiteracy is so great, that they do not understand the dangers this president and his party portend. The citizen who does not know what the Constitution says is poorly-equipped to know when its provisions are stripped away.
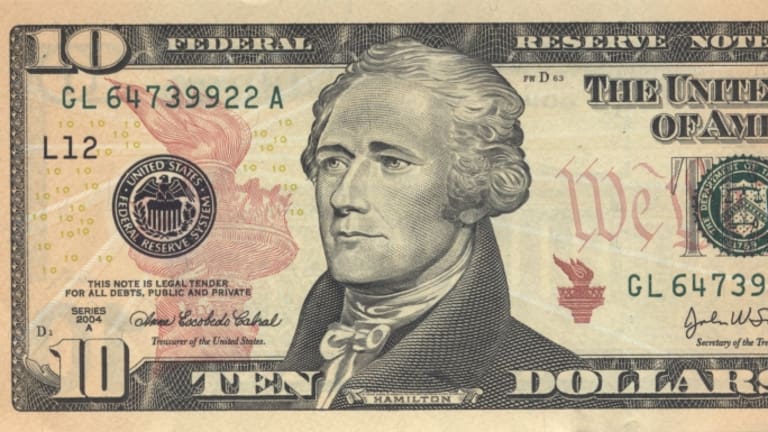
AS A STUDENT OF THE REVOLUTION, I fear for the future. The founding generation knew that republics did not last for log and that corruption, selfishness, and ignorance posed fundamental threats. Many of their most momentous debates centered on questions of how to avoid these threats. As he watched the government struggle during the Confederation period, Alexander Hamilton expressed his distrust of the people. They could not govern responsibly. “All men of respectability who have been witnesses of the despotism and iniquity of the legislature, are convinced that the principal people in the community must for their own defense, unite to overset the party I have alluded to.” High stakes were involved, he felt. “The safety of all those who have something to lose,” he wrote, “calls upon them to take care that the power of the government is intrusted to proper hands.” He called for a much more powerful central government than was established by the Philadelphia Convention in 1787. When he became George Washington’s Secretary of the Treasury, he argued for policies of broad political significance.
Admittedly, it has been a long time since I read in any depth in Hamilton’s work. I am not as up-to-date on the literature of the 1780s and 1790s as I want to be. Still, it seems to me that Hamilton’s experience during the war had convinced him of the necessity for a vigorous government. He did not believe that He did not believe that one could rely on “Virtue” as the basis for a framework of government. He believed, in fact, that mankind was in general so selfish and ambitious that virtue alone could never provide the basis for a system of government. A government based on virtue assumed that people would think of the common good. Hamilton thought all of that was nonsense.
Government should appeal, he argued, to the well-born, the wealthy, and the able if it were to succeed. He considered these people a sort of natural aristocracy. Hamilton admired Great Britain and especially its commercial power. He wanted the same for America. He thought that this could be obtained most easily by pursuing two general policies: First, Hamilton wanted to use the power of the federal government to encourage manufacturing and commerce in order to make the United States economically strong and independent for Europe. He did not believe the United States could remain politically independent of Europe if it remained economically dependent. It must move beyond a colonial economy. Second, he wanted to link the rich and the wealthy to the government. These were the secure part of the body politic, he believed, the stable people most capable of taking the long-term view of the issues. These were the stable people.
How to achieve this? Hamilton laid out his program in his Report on the Public Credit, a white paper arguing that the government could take steps to strengthen the nation’s finances. His program consisted of two things: Funding and assumption, and the creation of a National Bank. Hamilton asserted that the government needed two things in order to prosper: revenue and Credit. It needed capital, money, but it also needed the faith of merchants and other governments that it would repay its debts. Without that faith, the government would lack the ability to borrow money, which sometimes governments have occasion to do.
All told, the Confederation had accumulated a debt of $52 million dollars. Hamilton said that this debt should be paid in full, or funded. Also, the several states had accumulated debts of $25 million. He believed that the federal government should assume responsibility for these debts and pay them in full. How would this work? For funding, Hamilton asserted that all those holding certificates of the confederation debt, these bonds, would be paid the full face value for those notes. The money for funding this debt would come from the issuance of new notes.
Holders of the debt would be paid in full, unless they preferred to receive the newly issued notes. These notes would serve as a form of currency, so long as confidence existed that the government would continue to survive. For the assumption of state debts, the same principal applied. The United States would pay to the holders of state paper the face value or, if they chose, to deliver to them new bonds.
What was Hamilton after?
He claimed that the failure of certain states to honor their obligations undermined American credit in overseas markets. He saw the assumption of state debts as a means for the federal government to secure the gratitude and loyalty of state creditors by honoring their claims before the states could manage to pay them. These creditors would look to the new national government, rather than the state governments, securing the allegiance of an important class of citizens.
Hamilton also wanted to establish a national bank. Banks, he argued, could create capital. A national banking institution was an unprecedented idea. Hamilton recognized that a large financial institution could act as the fiscal agent of the United States government.
This bank would be a joint public-private venture. 4/5 of the stock of the national bank would be held by private investors. The bank, he argued, was a public institution, thus the stock ought to be available to the public.
There were many critics of the Bank. There was, many of these critics contended, nothing in the Constitution that authorized the United States government to establish a national banking institution. The Bank took the notion of implied powers too far.
Congress deadlocked over Hamilton’s financial program. Many southern states, especially Virginia, were unhappy about assumption, because they had already paid their debts and did not relish the prospect of possibly being taxed to assist heavily indebted states like Massachusetts.
James Madison and Thomas Jefferson met with Hamilton. They reportedly worked out a compromise over dinner. They agreed to support his financial program if, after ten years, Hamilton agreed to support the notion of establishing the permanent seat of the national capitol in the south. .Funding and assumption passed the Congress, the Bank of the United States was granted a 20-year charter, and the national capital was built in the District of Columbia.
PERHAPS HAMILTON INJECTED A POWERFUL STRAIN OF CYNICISM into the American political system. His distrust in the capacity of ordinary people to rule responsibly is powerful and he stated it frequently. I have not read a lot on Hamilton recently, but the thing that strikes me as I reflect on this period we have entered is that he did expect those chosen to lead in the republic’s extended sphere to be wise, and men of character and integrity. It seems like we the people have chosen poorly lately, and part of that is our fault. And if the President is reelected, whether by fair means or foul, I am not sure the system can be saved. Soon, we are told, 50% of the American people will live in 8 states. Half the population will have 16 senators, and half will have sixty-four. Show me a political leader with vision calling for reform of these deep structural problems, and I will show you a woman or a man marginalized in our political life, denounced as a dreamer, a demagogue, or a “socialist.”
MY DAUGHTER IS FINISHING HER first year of college. At her high school graduation ceremony eleven months ago, the Superintendent opened his remarks to the graduates with an apology. I am sorry, he said, on behalf of my generation, for leaving your generation with so many problems to solve. We failed you. But looking out at that auditorium filled with kids, he expressed some optimism, too. Your generation is better than ours is so many ways. Save us, he said. You can do it.
I found this profoundly moving. We need to help these young people. We need to encourage them to be braver than us. These young people, after all, now live in a world that you and I have helped to create for them where too many people confuse their feelings and their fears for facts, where being smart and engaged and critical and willing to ask questions can make one an object of scorn. They live in a world as well where complexity is so often dismissed, where big and difficult answers to the big questions are avoided, that asking these sorts of questions can take a certain amount of courage. Rational, reasoned, and just public policy is difficult if not impossible without an informed, engaged, and rationally-thinking public willing to ask tough questions, to engage.
Here is what a student of mine wrote a couple of years ago for her Humanities final. The assignment I gave asked students to write about human nature, justice, and the problem of evil, as they contemplated an article by Roger Rosenblatt I have mentioned many times on this blog, and works by Sophocles, Plato, Thucydides, Augustine, More, the Bible, and Shakespeare. “The question remains,” this very talented student wrote, “how do we account for all of the hatred, violence, and injustice that we witness? What words do we use to describe it? How can we possibly rationalize it and make sense of it? Where do we find its opposite in the world, and how do we eagerly point at that, so as to say, ‘See, this is also us. This is also me.’
“In a world and a human history overwhelmed by hatred, violence, and injustice, what counters it, I argue, is love, compassion, faith, and the courage to rise above it.”
I agree with the superintendent. This rising generation is already better than us in important ways—its open-mindedness, its tolerance, its acceptance of difference. I really believe that. As educators we must encourage courage. We have a lot of influence. Or at least we have the potential to be highly influential: a cruel or an uncaring word from us, for example, even when cast off thoughtlessly or uncritically, or because we are stressed out or too busy, can do so much damage, while a simple kind word, a single note of encouragement, can do something that these students might remember for the rest of their lives, something that can help them write a beautiful life story.
So let’s do better. Let’s encourage fearlessness, even where we have failed to demonstrate it ourselves. Each and every day, I have the opportunity, if I choose to truly be present, to truly listen, to be awed by their achievements, humbled by the obstacles they have overcome to get to this college, inspired by their creative thinking, pushed by their challenging questions, and amazed by the alacrity with which so many of them seek out injustice, attempt to correct oppression, and in thousands of small ways show the vital courage to make the world—our world—a better place. Our future is in their hands.